Class (biology): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
added content from Wikipedia |
added chart |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Biological classification L Pengo.svg|thumb|158px|right|The hierarchy of biological classification's major eight taxonomic ranks. Intermediate minor rankings are not shown.]] | |||
A '''class''' is the [[taxonomic rank]] in the [[biological classification]] of organisms in [[biology]] below [[phylum (biology)|phylum]] and above [[Order (biology)|order]]. | A '''class''' is the [[taxonomic rank]] in the [[biological classification]] of organisms in [[biology]] below [[phylum (biology)|phylum]] and above [[Order (biology)|order]]. | ||
The orders of taxonomy are [[life]], [[Domain (biology)|domain]], [[kingdom (biology)|kingdom]], [[phylum]], [[class (biology)|class]], [[order (biology)|order]], [[family (biology)|family]], [[genus]], and [[species]]. | The orders of taxonomy are [[life]], [[Domain (biology)|domain]], [[kingdom (biology)|kingdom]], [[phylum]], [[class (biology)|class]], [[order (biology)|order]], [[family (biology)|family]], [[genus]], and [[species]]. | ||
Revision as of 22:31, 25 February 2009
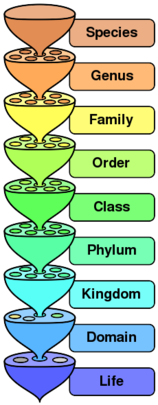
A class is the taxonomic rank in the biological classification of organisms in biology below phylum and above order. The orders of taxonomy are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
For example, Mammalia is the class used in the classification of dogs, whose phylum is Chordata (animals with notochords) and order is Carnivora (mammals that eat meat).
See also
External links
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Class_(biology) (this page GNU FDL Wikipedia)